What Does Remastered Mean? The Truth Behind Audio Restoration

Introduction
You are scrolling through Spotify or Apple Music, looking for a classic album by Pink Floyd, Queen, or Nirvana. You find the album, but the title has a tag next to it: (2011 Remaster). You might wonder: Does this sound better? Is it just louder? Or is it a completely different recording?
For the average listener, the remastered meaning is often shrouded in marketing buzzwords. Audio engineers, however, view it as a specific technical process. This guide provides a definitive answer to what remastered music means, breaking down the difference between restoration, remixing, and re-recording, and explaining why your favorite songs keep getting updated.
Direct Answer
What does remastered mean?
In short, a remaster is the process of taking the original final mix of a song (the “Master Tape”) and polishing it to meet modern sound quality standards. It is not a new recording.
Think of it like restoring an old painting in a museum. The restorer carefully cleans off the dust, brightens the faded colors, and puts it in a new frame. They do not paint over the original image; they simply reveal the detail that was always there but obscured by time. When people ask what is a remastered song, you are asking about a vintage recording that has been optimized for modern playback devices like smartphones and high-fidelity streaming services.
The Technical Definition (Master vs. Remaster)
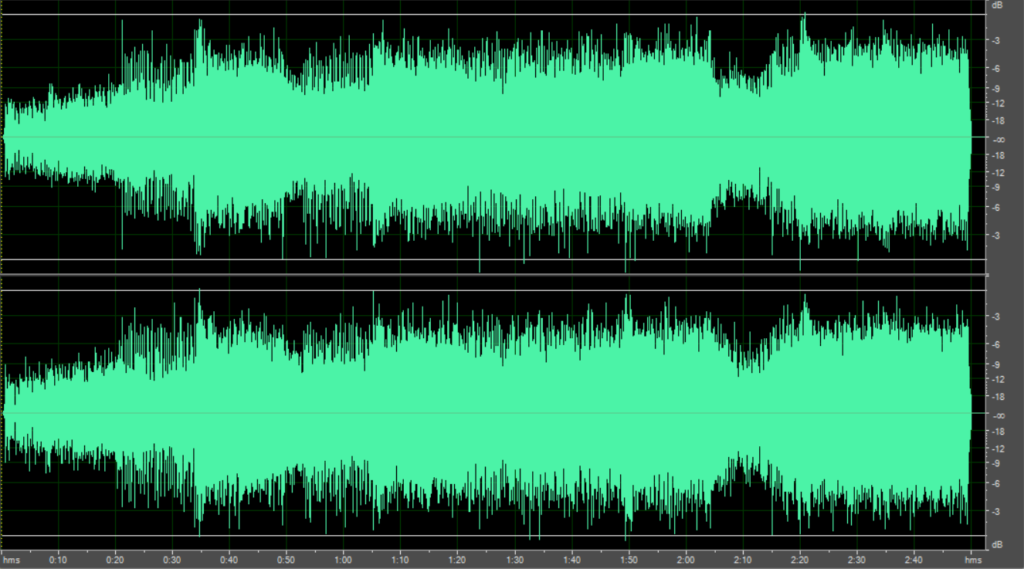
To understand what remaster means, one must first understand what a “Master” is.
- The Master Tape: This is the final, approved version of a song after the mixing process is complete. In the 1960s and 70s, this was a physical magnetic tape.
- The Problem: Older masters were engineered for the limitations of vinyl records. Vinyl cannot handle excessive sub-bass or extreme high frequencies without the needle jumping out of the groove. Therefore, older masters often sound “thin” or quiet when played on modern digital systems.
- The Solution: The remastering process involves going back to that original source tape and transferring it to digital with new EQ and compression settings suited for digital formats, which have no physical limitations.
The Remastering Process: Step-by-Step
When an engineer is tasked to define remaster work for a legacy artist like The Beatles, the process follows a strict technical workflow.
1. High-Resolution Transfer
The original analog tapes are fragile. The engineer plays them back on a meticulously calibrated tape machine and captures the audio into a digital workstation at a very high sample rate (typically 192kHz / 32-bit float). This captures every nuance of the magnetic signal.
2. Restoration (De-noising)
This is a critical part of remastered audio tracks. Old tapes have “hiss,” clicks, and pops. Engineers use spectral repair software to surgically remove these artifacts without damaging the music.
3. EQ & Compression (Enhancement)
This is where the sonic character changes.
- EQ: The engineer might boost the high frequencies (“air”) to make the cymbals sound crisper, or boost the low end (60Hz) to make the kick drum punchier.
- Compression: This glues the track together, making it feel tighter and more consistent.
Check also our mixing cheat sheet guide to make the most from your sound.
4. Limiting (Loudness)
Finally, the volume is raised to compete with modern pop songs. This ensures that when a listener shuffles between a 1970s track and a 2026 track, they don’t have to reach for the volume knob.
Remaster vs. Remix vs. Remake: What’s the Difference?
Confusion often arises regarding remastered music versus other types of re-releases.
| Term | Definition | Example |
| Remaster | The original stereo mix is polished. No instruments are added or changed. | Pink Floyd – The Dark Side of the Moon (2011 Remaster) |
| Remix | The engineer goes back to the individual tracks (Multitrack). They can change the balance (e.g., make vocals louder, remove a guitar). | The Beatles – Sgt. Pepper’s (2017 Stereo Remix) |
| Remake | The artist goes back into the studio and records the song again from scratch. | Taylor Swift – Fearless (Taylor’s Version) |
So, what does it mean in the context of a song? It means you are hearing the exact same performance from 1980, just clearer. A Remake means you are hearing a performance from 2026.
The “Loudness War” Controversy (Is Newer Always Better?)
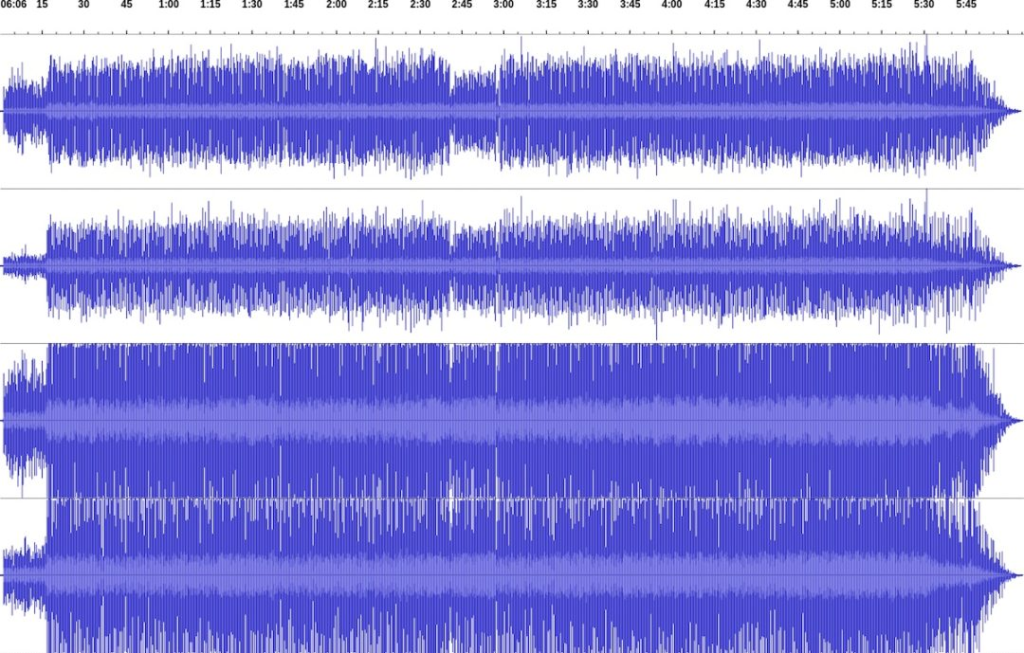
But are there any downsides of remastered albums of beloved artists? One truly must address the controversy. Not all remasters are good.
In the 1990s and 2000s, the industry became obsessed with loudness. This phenomenon, known as the “Loudness War,” led engineers to use aggressive digital limiters.
- Dynamic Range: The difference between the quietest and loudest parts of a song.
- The Brickwall: Aggressive remastering crushes the peaks of the waveform. The drums lose their punch, and the music becomes a constant wall of noise.
In this context, the remastered definition can sometimes imply “ruined by over-compression.” Audiophiles often prefer the original, quieter CD releases (like those from the 1980s) because they retain the natural dynamics of the performance.
Why Do Artists Remaster Albums?
If the original was good enough, what is a remaster for? There are three main drivers:
- Format Updates: An album mastered for a cassette tape sounds muddy on Spotify. Remastered means updating the EQ curve for the medium people are actually using.
- Anniversaries: Releasing a “20th Anniversary Edition” is a prime marketing opportunity to resell the back catalog to fans.
- Copyright Preservation: In some jurisdictions, updating a master can help extend or clarify copyright claims on the recording.
Check also our MP3 vs MP4 guide to see the difference between two giants of formats.
Gaming & Film Context (Briefly)
The term is not exclusive to music. Here’s the definition in the context of video games:
- Game Remaster: The developers take the original game engine and update the textures to 4K resolution, improve the lighting, and increase the frame rate. The underlying code remains the same (e.g., The Last of Us Remastered).
- This differs from a Remake (e.g., Resident Evil 4 Remake), where the game is built from the ground up with new mechanics.
Conclusion
So, what does remastered mean? It is the bridge between the past and the present. It is the technical process of transferring vintage analog art into the crisp, high-definition digital world.
At its best, a remaster breathes new life into a classic, allowing you to hear details like the squeak of a bass drum pedal or the breath of a singer that were previously buried in tape hiss. At its worst, it is a victim of the loudness war. When choosing which version to listen to, trust your ears—sometimes the shiny new remastered version is definitive, and sometimes the original holds the true magic.
FAQ
What does remastered mean in a song title on Spotify?
It indicates that the audio file you are streaming has been processed from the original master tapes to improve sound quality, clarity, and volume compared to the original vinyl or CD release.
Does remastered mean re-recorded?
No. Remastered means the original recording was polished. If the artist re-recorded the song, it would be called a “Re-recording” or “Remake” (e.g., Taylor’s Version).
Is a remastered song better quality?
Generally, yes. The definition of remastered implies higher clarity and less noise. However, some fans dislike modern remasters if they are made too loud, which can reduce the dynamic impact of the drums.
What does remaster mean for the volume of the track?
Almost always, a remaster will be louder than the original release. Engineers use digital limiters to ensure the track reaches competitive streaming levels (e.g., -14 LUFS).
Remaster meaning vs. Remix?
A remaster works with the final stereo file (2 tracks). A remix works with the original separate instrument tracks (24+ tracks) and changes the balance of the song.